lat_lonedit
Geo-queries are usually performed by plugging the value of
each geo_point field into a formula to determine whether it
falls into the required area or not. Unlike most queries, the inverted index
is not involved.
Setting lat_lon to true causes the latitude and longitude values to be
indexed as numeric fields (called .lat and .lon). These fields can be used
by the geo_bounding_box and
geo_distance queries instead of
performing in-memory calculations.
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "geo_point",
"lat_lon": true 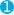 }
}
}
}
}
PUT my_index/my_type/1
{
"location": {
"lat": 41.12,
"lon": -71.34
}
}
GET my_index/_search
{
"query": {
"geo_distance": {
"location": {
"lat": 41,
"lon": -71
},
"distance": "50km",
"optimize_bbox": "indexed"
}
}
}
}
}
PUT my_index/my_type/1
{
"location": {
"lat": 41.12,
"lon": -71.34
}
}
GET my_index/_search
{
"query": {
"geo_distance": {
"location": {
"lat": 41,
"lon": -71
},
"distance": "50km",
"optimize_bbox": "indexed"  }
}
}
}
}
}
Setting | |
The |
Whether the in-memory or indexed operation performs better depends both on your dataset and on the types of queries that you are running.
The lat_lon option only makes sense for single-value geo_point
fields. It will not work with arrays of geo-points.